sop for Risk Management
1.0 Objective
To lay down a Procedure for assessing the level of qualification to be conducted based on
the risk identification, analysis, evaluation and control which could impact critical quality
attributes of product as per FMEA principle. To define the degree of impact on subjected
quality process to be qualified to enhance the implementation of risk control to the
acceptable level. To define a traditional impact assessment procedure to evaluate facility
subjected to technology transfer, process subjected to change control, deviation and
incident reporting etc based on identified regulatory and GMP compliance requirement and to
ensure changes in process variable, critical quality attributes and process control parameters
are adequately reviewed and approved as per product life cycle management.
2.0 Scope
2.1 This procedure applies to all critical steps of activity related to facility, personnel, material
and processing of ingredients during qualification of equipments to define predetermined process
variable and control parameters to achieve desired critical quality attributes.
2.2 This also applicable to the existing process and systems (equipment, facility, material, training and process)
which are perturbed from the existing validated state.
3.0 Responsibility
3.1 Head F&D: To ensure development of product following principle of product life cycle management.
3.2 Head Engineering: To perform risk evaluation and maintain facility and equipment related risk
evaluation report based on this procedure for qualification and preventive action.
3.3 Head Production: To ensure operation procedure / maintenance procedure and cleaning procedure
are defined based on development and validation of critical steps identified as per FMEA principle.
3.4 Person identified in QA: To ensure risk parameter adequately identified and controlled while
qualifying equipment & facility. To ensure that transfer of technology from F&D done as per protocol
which adequately assure the consistency of quality attributes.
3.5 Head QA: To evaluate the process of F & D studied adequately to ensure feasibility and
compliance as per regulatory requirement.
3.6 Head QA / designee is compliance of this SOP.
3.7 Risk Assessment Team: It ensures the identification, evaluation and control of risk with
respect to new product / facility as per FMEA principle and shall be approved by this team
whenever new product introduced into system.
3.8 In existing system it evaluates impact as per Risk Evaluation Checklist for Existing Process
(Annexure-2) and shall give clearance on changes / deviation / incident report / CAPA. The team
consists of Formulation Development Department / Production / Engineering / Validation / Quality Assurance.
4.0 Abbreviations and Definitions
SOP : Standard Operating Procedure
FMEA : Failure Modes and Effects Analysis
QA : Quality Assurance
QC : Quality Control
OOS : Out of Specification
w.r.t. : with respect to
No. : Number
CAPA : Corrective Action Preventive action
RA : Risk Assessment
F&D : Formulation & Development Department
DQ : Design qualification
URS : User Specification Requirement
PQ : Performance Qualification
RPR : Risk Priority Rate
VMP : Validation Master Plan
GMP : Good Manufacturing Practice
GLP : Good laboratory Practice
TTD : Technology Transfer Dossier
MRN : Mandatory Review Notice
5.0 Procedure
5.1 General Over view of Risk Management Process (Refer Annexure – 1).
5.2 Any process which affect control parameter / critical quality attributes are called critical steps
which shall affect quality of product directly / indirectly. This is applicable through out the
product life cycle management from development, qualification, implementation, control,
maintenance, review, and requalification to disposal.
5.3 Initiating a Quality Risk Management Process (By user / owner department).
5.3.1 Define – The user department (e.g. Production) or owner of system or equipment (e.g. Engineering or project)
shall define the problem and / or risk question, including pertinent assumptions identifying
the potential for risk based on ** input (e.g.: Bioburden) and *** out put (e.g.: Sterility compliance)
and control parameters of designed process flow (as per FMEA).
5.3.1.1 User department shall define the intermediate process* subjected to risk analysis
shall be noted for its existing control based on process variable and capability
with respect to available tools and functions.
5.3.1.2 The User department shall analyze the control existing to achieve desired performance
shall be analyzed to reduce the negative control by implementing adequate system in
personnel, equipment, material/critical component, facility and processing parameters.
5.3.1.3 For any type of risk evaluation the minimum document requires shall
comply as per section 5.3.1 to define the risk.
5.3.1.4 For new products the design of experiment based on product life cycle
management and the results of same documented in relevant documents shall be taken to ensure design compliance.
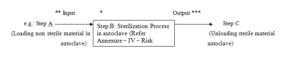
5.3.1.5 e.g.: ** Input: Bioburden from Process Categories like Personnel, Process, Equipment Failure,
Primary Packaging Failure, Component Failure, Facility / Utilities.
5.3.1.6 e.g.: *** Out put: Sterility test of product.
5.3.1.7 e.g.: * Potential risk failures: Failure in sterility due to inadequate process control
parameter (specification, functional and performance).
5.3.2 Measure – Assemble background information and / or data on the potential hazard,
harm or human health impact relevant to the risk assessment. Back ground information
shall be from Design Qualification (DQ) and compliance details w.r.t. regulatory guidelines concerned.
5.3.3 Analyze – Analyze the data with the help of subject matter experts of cross functional team.
Analyze URS verses DQ for feasibility and DQ verses Installation Qualification (IQ) for specification
compliance, IQ verses Operational Qualification (OQ) for functional capability which needs to
comply w.r.t. regulatory compliance and compliance on input and output material feasibility.
PQ verses product specification on intended scope of validation.
5.3.4 Verify – Verify the feasibility of control as per the impact and control addressed through
new control over the existing system to achieve the reliable consistent quality attributes as per PQ.
5.3.5 Implement / Improvement – Ensure the risk assessment team verified risk
assessment and risk control for its proper identification and adequate control during
development of new process for proper implementation. Whereas in existing process ensure the
changes done after proper impact assessment (as per risk assessment check list) to
enhance improvement in existing process.
5.3.6 Control – Ensure the risk control is approved as recorded in the risk register as per
Annexure – 4 (Risk Register) and not required any amendment.
5.4 Risk Assessment Team Evaluation steps:
5.4.1 The team shall evaluate the following during implementation of new process / during the
validation of any system and during evaluation of changes from existing system.
5.4.2 This shall be addressed through subject-wise discussion (among members of this team) based
on the documents in its place as per VMP during validation / qualification requirement
before execution of protocols after its approval.
5.4.3 For new products relevant change control with TTD and validation protocol shall be the
basis for discussion. Final conclusion shall be recorded in the risk register as per
Annexure – 4 (Risk Register) and in risk evaluation check list for existing process (Annexure – 2)
as and when triggered by Change control, Deviation, Incident report, CAPA and others.
5.4.4 Risk Assessment by the team shall ensure the proper identification of hazards and the analysis and
evaluation of risks associated with exposure to those hazards are relevant and appropriate to
the operation. General Overview of Risk assessment refer as per Annexure –1.
5.4.5 Risk identification by team shall ensure systematic use of information to identify hazards
referring to the risk question or problem description in place. Shall verify information such as
historical data, theoretical analysis, informed opinions, and the concerns of stakeholders.
5.4.6 Risk analysis by team shall ensure estimation of the risk associated with the identified hazards
done by qualitative or quantitative process of linking the likelihood of occurrence, severity of harms and detection principle.
5.4.7 Risk evaluation by team ensure the identified and analyzed risk against given risk criteria are
compared. Risk evaluations consider the strength of evidence for all three of the severity, occurrence, and detection.
5.4.8 Risk communications by team ensure it is communicated by sharing of information
about risk and risk management between the decision makers and others. Ensure QA activity
extended to change implementation and post implementation impact through change control
or CAPA system. It shall be done through change and deviation review as per Risk review
section 6.4.9 by the concerned Risk Assessment Team.
5.4.9 Risk Review:
5.4.9.1 QA shall ensure a review system by the risk assessment team in place for existing process.
A mechanism to review or monitor events shall be implemented. The output
(after change or deviation implementation) / results of the risk management process shall be reviewed to
take into account new knowledge and experience.
5.4.9.2 Once a quality risk management process has been initiated, that process should
continue to be utilized for events that might impact the original quality risk management
decision, whether these events are planned (e.g., results of product review, inspections,
audits, change control) or unplanned (e.g. root cause from failure investigations, recall).
The frequency of any review should be based upon the level of risk and shall be reviewed
by risk assessment team whenever requalification or revalidation takes place.
5.4.10 Risk Control and Conclusion: Shall ensure the risk evaluation and risk control procedure
followed same modalities until arriving the conclusion as per Annexure-4 (Risk Register) while
applying factors S-Severity, O-Occurrence and D-Detection.
5.4.10.1 Severity (S): Impact of Failures and its Consequences (Severity-S), Impact or Severity
of the Failure and its Consequences on the Product and Instrument.
5.4.10.1.1 High – If impact of failure and its consequences directly affects the product quality.
5.4.10.1.2 Medium – If it affects the interdependent system but effect product quality attributes
which is not a threat to the patient.
5.4.10.1.3 Low – If preventive program can avoid the occurrence and the out put shall be evaluated
by a detection system or mechanism which shall incur loss of quantity only.
5.4.10.2 Occurrence (O): It is likelihood that the occurrence of the process step failures.
This shall be evaluated by occurrence number.
5.4.10.3 High – Unpredictable frequency.
5.4.10.4 Medium – Can be controlled by preventive maintenance.
5.4.10.5 Low – Very rarely occur and can be detected.
5.4.11 Failure Detection and reduction controls (D): If the function / item fail, detection of failure
enabled to propose corrective action or control measures.
5.4.11.1 High – Cannot be detected unless to check the component / operation / output.
5.4.11.2 Medium – Can be detected during observation of operational parameters.
5.4.11.3 Low – Can be detected by routine calibration / product quality trend.
5.4.12 RPR (Risk Priority Rate): The study of the Risk involved in operation of the
Equipment / Utilities is done for all the Critical functions. Each factor is being measured as below:
5.4.12.1 Risk Priority Rate (RPR) = S x O x D
5.4.12.2 Note: S – Severity, O – Occurrences, D – Detection
| Measures | Severity Rating | Occurrences Rating | Detection Rating |
| High (H) | H | H | H |
| Medium (M) | M | M | M |
| Low (L) | L | L | L |
5.4.13 Risk Register : (Refer Annexure – 4 – for format issuance and
Annexure – 5 – Filled format for reference)
5.4.13.1 The above factors are applied based on Function (operational requirement) / Item of the
Equipment(design requirement) / Utility Impact / critical quality attributes (performance requirement)
and finally each function RPR is drawn by the Formula: (S x O x D = RPR) according to the critical control function.
5.4.13.2 The RPR results for all functions / items which will be fitted acceptable to the ranges / limits by risk reduction
if necessary and the qualification requirements will be based on the RPR categories as follows.
5.4.13.3 Sum of Risks shall be calculated on the following basis:
- H x H x H = H, H x H x L = H, H x H x M = H
- H x M x M = M, H x L x L = L, H x M x L = M
- M x M x M = M, M x M x L =L, M x L x L = L
- L x L x L = L
5.4.13.4 All existing control if considered low risk (with respect to Severity / Occurrence / Detection)
shall be considered for a lineant validation approach with respect to that.
5.4.13.5 But any item / function / critical quality attribute found to be rated as risk RPR of
Medium / High as per existing control necessary process control shall be done to bring down to
low under reduction control. If it is brought down to medium a justification based on more
frequent calibration or preventive maintenance shall be accepted based on situation and
shall go for stringent validation approach with an appropriate requalification for critical component changes.
5.4.13.6 A revalidation frequency of limited or complete shall be incorporated in the Validation
programme also. But no time any equipment with high RPR (after risk reduction) is allowed for
validation if it is for critical process or evaluation purpose.
5.4.13.7 Risk Register shall have the number with prefix RR ——- followed by change control
number / deviation number / incident report number / equipment
number / system number / Installation protocol number as applicable.
5.4.13.8 The risk register shall have the columns and rows as mentioned in the Annexure –
4. The information to be filled also given in Annexure – 5 as an example. (Refer Annexure – 5).
5.4.13.9 The risk register is not applicable to new product development. In case the impact
assessment triggered any studies required it shall be addressed through the design of
experiment as per product life cycle management which shall be suitably done by development team.
5.5 Risk Identification, Evaluation and Control for Existing Process:
5.5.1 Initiation of Risk Assessment: The process of identifying changes due to
unplanned deviation / Change Control / Incident Report / Risk reporting
/ CAPA / Audit review / Annual product review / any deviation including product
complaint and recall shall be as per Annexure – 3 (Risk Management Approach in Existing Process).
5.5.2 Risk evaluations for existing process which shall contain risk assessment of
identified process change wide refer Annexure – 2.
5.5.3 It shall determine the requirement of risk evaluation and shall be closed in the
respective Change control / Deviation / Incident Process / CAPA.
5.5.4 If risk evaluation required it shall be addressed through the Risk Register as per
Annexure-4. Risk evaluation checklist shall have the number RA —- followed by change
control number / deviation number / incident report number as applicable
(Refer Annexure – 2 – Risk Evaluation Check List for Existing Process).
6.0 Forms and Records
6.1 General Over view of Risk Management Process – Annexure-1
6.2 Risk Evaluation Check List for Existing Process – Annexure-2
6.3 Risk Management Approach in Existing Process – Annexure-3
6.4 Risk Register (Format for issuance) – Annexure-4
6.5 Risk Register (Filled format for reference) – Annexure-5
7.0 Distribution
7.1 Master copy – Documentation Cell (Quality Assurance)
7.2 Controlled copies – Quality Assurance, Production, Warehouse,
Quality Control, Personnel & Administration, Engineering
8.0 History
| Revision Number | Details For Change |
Reason for Revision |
| 00 | New SOP | NA |
- process validation protocol for methylcobalamin niacinamide and pyridoxine injection
validation protocol of sterility test
sop for Analytical Method Transfer
Protocol for hold time study of sterile garments
sop for swab sampling for validation of clean surfaces
cleaning validation maco and noel calculation formula
sop for performance qualification for analyst
Sop for Validation report for disinfectant efficacy
Sop for Method validation report for bacterial endotoxin test
Sop for method validation microbiology sterility testing
sop for validation report for preservative efficacy test
sop for Protocol cum report for efficacy qualification of uv light
sop for validation protocol for uv light efficacy of dpb & laf
sop for cleaning validation protocol tablet manufacturing equipment
sop for cleaning validation protocol ointment manufacturing equipmentconcurrent process validation for rabeprazole ec and domperidone sr capsules
sop for Validation for cleaning procedure liquid injection
sop for Validation for cleaning procedure dry powder injection
Preparation Approval Control and Distribution of Master Formula Records
calibration policy for equipment and instruments
evaluation Sampling of Raw Materials questionnaire
training evaluation questionnaire
sop for approval of Contract Parties
sop for Operation and Cleaning of Purified Water Generation System
sop for Storage of Standard Weights
-
process validation protocol for methylcobalamin niacinamide and pyridoxine injection
validation protocol of sterility test
sop for Analytical Method Transfer
Protocol for hold time study of sterile garments
sop for swab sampling for validation of clean surfaces
cleaning validation maco and noel calculation formula
sop for performance qualification for analyst
Sop for Validation report for disinfectant efficacy
Sop for Method validation report for bacterial endotoxin test
Sop for method validation microbiology sterility testing
sop for validation report for preservative efficacy test
sop for Protocol cum report for efficacy qualification of uv light
sop for validation protocol for uv light efficacy of dpb & laf
sop for cleaning validation protocol tablet manufacturing equipment
sop for cleaning validation protocol ointment manufacturing equipmentconcurrent process validation for rabeprazole ec and domperidone sr capsules
sop for Validation for cleaning procedure liquid injection
sop for Validation for cleaning procedure dry powder injection
Preparation Approval Control and Distribution of Master Formula Records
calibration policy for equipment and instruments
evaluation Sampling of Raw Materials questionnaire
training evaluation questionnaire
sop for approval of Contract Parties
sop for Operation and Cleaning of Purified Water Generation System
sop for Storage of Standard Weights
sop for Verification of Weighing Balance
-
Sop for Submitting of Leave Application
sop for Accident Management Procedures
sop for Accident Management Procedures
Cleaning and colour coding of Factory Apparel (Clothes)
Job Responsibilities of Key Personnel
sop for Maintenance of Building
Destruction of Batch Production and Control Records BPCR
Procedure for Sampling of Rinse water Swab
Cleaning Validation of Equipment
Measurement and Recording of Temperature and Relative Humid
Sampling of Product at Intermediate Stages
Approval of Overprinting on Packing Material
sop for Procedure for Reprocessing
Preparation and Control of Master Batch Production and Control record
Issuance and Retrieval of Control documents
Calibration Policy for equipment
procedure for batch numbering system for products
sop for Handling of Incident during operation
Procedure for Allocation of Numbers for Machine Equipment
Validation and Qualification Facility System and Equipment
In-process Checks During Packing Operation
Procedure for Issuance of Extra Raw Material Packing Material