General Test Procedure Density and Tapped Density
- Purpose
- This procedure is applicable to all incoming Raw materials.
- Apparatus
 3. Reagents
3. Reagents3.1`None4.0 Procedure: The apparatus consists of the following:
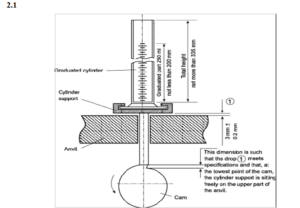
- A settling apparatus capable of producing in 1 min 250 ± 15 taps from a height of 3 ± 0.2 mm. The support for the graduated cylinder, with its holder, has a mass of 450 ± 5 g;
- 250 ml graduated cylinder (2 ml intervals) with a mass of 220 ± 40 g.
5.0 Method
5.1 Into the dry cylinder, introduce without compacting 100 g of the substance to be examined.
If this is not possible, select a test sample with an apparent volume between 50 ml
and 250 ml and specify the mass in the expression of results. Secure the cylinder in its holder.
Read the unsettled Apparent Volume V0 to the nearest milliliter. Carry out 10, 500 and 1250
taps and read the corresponding volumes V10, V500 and V1250, to the nearest milliliter.
If the difference between V500 and V1250 is greater than 2 ml, carry out another 1250 taps.
Expression of the results:
Apparent Density/Bulk Density (Before settling) = m/V09g/ml)
Tapped Density (After settling) = m/V1250 (or) m/V2500 (g/ml)
Where,
m = Weight of the substance to be examined
V0 = Bulk volume before settling
V1250 = Apparent volume after settling (or) V2250
5.2 Bulk Density is determined by measuring the volume of a know mass of powder sample that has been passed through a screen into graduated cylinder (Method I) or through a volume-measuring apparatus into a cap (Method II).
5.2.1 Method I: Measuring in a Graduated Cylinder: Unless otherwise specified, pass a quantity of material sufficient to complete the test through1.00 mm screen (No. 18) to beaker up agglomerates that may have formed
during stored into a dry 250 cylinder introduce, without compacting, approximately 100g of test sample,M,
weight with 0.1% accuracy. If it is not possible to use 100g, the amount of the test sample and the volume of the
cylinder may be modified and the test condition specified with the results. Select a sample mass having an
untapped apparent volume of 150ml to 250ml.A 100ml cylinder is used for apparent volume between 50ml and
100ml.Carefully level the powder without.
M – Weight of sample taken in g compacting, if necessary, and read the unsettled
Apparent Volume
Vo – to the nearest graduated unit.
Calculation the bulk density, in g per ml, by the formula:

Generally replicate determinations are desirable for the determination of this property.
5.2.2 Method II: Measurement in a Voltmeter: Allow an excess of powder to flow through the apparatus into the sample receiving cup until it overflows, using a minimum of 25 cm3 of powder with the square cup 35cm3 of powder with the cylindrical cup. Carefully scrape excess powder from the top of the cup by smoothly moving the edge of the blade of a spatula perpendicular to and in contact with the top surface of the cup, taking care to keep the spatula perpendicular to prevent packing or removal of powder from the cup, remove any material from the sides of the cup, and determine the weight, M, of the powder to the nearest 0.1 %.
Calculation the bulk density, in g per ml, by the formula:

Generally replicate determinations are desirable for the determination of this property.
5.3 Tapped Density: Tapped Density is achieved by mechanically tapping a measuring cylinder containing a powder sample. After observing the initial volume, the cylinder is mechanically tapped, and volume reading is taken until little further volume change is observed. The mechanical tapping is achieved by raising the cylinder and allowing it to drop under its own weight a specified distance by either of two methods as described belowDevies that rotate the cylinder during tapping may be preferred to minimize any possible separation of the mass during tapping down.
5.3.1 Method I: Unless otherwise specified, pass a quantity of material sufficient to complete the test through1.00 mm screen (No.18) to break up agglomerates that may have formed during storage. Into a dry 250ml glass graduated cylinder (readable to 2ml) weighing 220 ± 44gm
and mounted on a holder weighing 450 ± 10gm introduce without compacting, approximately 100g of the test sample, M, weiged with 0.1 % accuracy. If it is not possible, use 100g, the amount of the test sample may reduced and the volume of the cylinder may be modified by using a suitable 100ml graduated
cylinder (readable to 1ml) weighing 130 ± 16gm and mounted on a holder weighing 240 ± 12g. the
modified test condition is specified with the results. Carefully level powder without compaciting,
if necessary and read the unsettled apparent volume, V0, to the nearest graduated unit.
Mechanically tap the cylinder containing the sample by raising the cylinder and allowing it to
drop under its own weight using a suitable mechanical tapped density tester that provides a fixed
drop of 14±2mm at a nominal rate of 300 drops/minutes. Unless otherwise specified, tap the
cylinder 500 times initially and measure the tapped volume, a to the nearest graduated unit.
Repeat the tapping an additional 750 times and measure the tapped volume, Vb, to the nearest
graduated unit (Note: fewer taps may appropriate, if validation, for some powder).
If the difference between two volumes is less than 2% Vb, in the final tapped volume,
Vf.Repeat in increments of 1250taps, as needed, until the difference between succeeding
measurements is less than 2 %.
Calculation the tapped density, in gram per ml, by the formula

Generally replicate determinations are desirable for the determination of this property.
-
-
- Method II: Proceed as directed under method except that a suitable mechanical tapped density tester that provides a fixed drop of 3mm (± 10%) at a nominal rate of 250 drops per minutes is used.
-
- Reference
- None
- Revision History
-
Revision No.
Details of Changes
Reason for change
00
New GTP
NA
Standard testing procedure of Iron Sucrose Injection
Standard testing procedure lactose
Standard testing procedure mefenamic acid
standard testing procedure domperidone
standard testing procedure flavour mixed fruit
standard testing procedure dicyclomine hydrochloride
Standard testing procedure honey pure
standard testing procedure dextromethorphan hydrobromide
standard procedure of levocarnitine injection
Analysis of Ivermectin Suspension
standard testing procedure artemether injection
standard testing procedure artemether injection
standard testing procedure Carbocisteine syrup
standard testing procedure Phytomenadione injection
standard testing procedure serratiopeptidase
standard testing procedure starch IP
standard testing procedure sucrose refined sugar
standard testing procedure titanium dioxide
standard testing procedure tramadol hydrochloride
standard testing procedure zinc sulphate
standard testing procedure croscarmellose sodium
standard testing procedure colour erythrosine supra
standard testing procedure magnesium hydroxide
standard testing procedure diclofenac sodium
standard testing procedure dibasic calcium phosphate
standard testing procedure cyanocobalamin
standard testing procedure cholecalciferol
standard testing procedure Calcium carbonate oyster shell powder
standard test procedure Calcium Citrate
standard testing procedure Bronopol
standard testing procedure Bromhexine Hydrochloride
Standard Testing Procedure diclofenac sodium injection
Standard Testing Procedure Drotaverine Hydrochloride injection
analysis of Procyclidine HCl 5 mg Tablet
analysis of silodosin 8 mg capsule
Method of Analysis Ceftriaxone and Sulbactam For Injection
Analysis of Glimepiride and Metformin Hydrochloride (SR) Tablets
General Test Procedure Melting Range and Freezing Point
General Test Procedure Weight per ML and Specific Gravity
General Test Procedure Distillation Range
General Test Procedure Non Volatile Matter and Residue on Evaporation
General Test Procedure Clarity of Solution
General Test Procedure Limit Test Chloride
General Test Procedure Limit Test Iron
General Test Procedure Limit Test Heavy Metals
General Test Procedure Water Soluble Substances