standard testing procedure croscarmellose sodium
Storage Requirements:
Store protected from light and moisture.
Sampling:
Sample from each container / bag, if the consignment is of 03 or less than three containers / bags. If the number of containers / bags is more than 03and are up to 100, sample at randomly using the formula root (n) +1 where n is the number of containers/bags in the consignment. For the consignment of more than 100 containers/bags, sample additional containers/bags for every 100 containers/bags and thereafter. Collect a minimum of 5g from each of the randomly selected containers/bags in to individually no toxic, self sealing transparent polyethylene bearing ‘Sample For Analysis label kept in another transparent self sealing polythene bag. After completion of sampling return rest sample on the same container. Collect control sample in Pet bottle/Glass bottle.
Quantity of Composite Sample:
50 g
Quantity of Control Sample:
2 X 50 g
Description: A white or greyish-white powder.
Solubility: Slightly soluble in water; insoluble in ethanol, ether and in other organic solvents.
Identification:
The substance under examination absorbs the methylene blue and settles as a blue, fibrous mass.
A reddish-violet colour develops at the interface.
The solution prepared from the sulphated ash in the test for Heavy metals gives reaction (a) of sodium salts.
pH: 5.0 to 7.0
Degree of substitution. Titrate with 0.1M sodium hydroxide until the colour turns to violet.
Sodium chloride and sodium glycollate: The sum of the percentage contents of sodium chloride and sodium glycollate is not more than 0.5 per cent, calculated on the dried basis.
Water soluble substances: NMT 10.0 per cent.
Heavy Metals: NMT 20ppm
Settling volume. The substance is homogeneously distributed
Microbial contamination: Total microbial count, not more than 103 bacteria and 102 fungi per gram.
Sulphated ash: NMT 14.0 to 28.0 % w/w
Loss on Drying: NMT 10.0 % w/w at 105º for 6 hours.
.
Description: A white or greyish-white powder.
Solubility: Slightly soluble in water
Insoluble in ethanol, ether and in other organic solvents.
Identification:
A. Shake 1g with 100ml of 0.0004 per cent w/v solution of methylene blue and allow to settle. The
Substance under examination absorbs the methylene blue and settles as a blue fibrous mass.
B. Shake 1g with 50ml of water. Transfer 1 ml of the mixture to a test-tube, add 1 ml of the mixture to a
Test-tube, add 1 ml of water and 0.05 ml of a freshly prepared 4.0 per cent w/v solution of œ–
Napthol in methanol. Incline the test –tube and add carefully 2 ml of sulphuric acid down the side so
That it forms a lower layer .A reddish –violet colour develops at the interface.
C. The solution prepared from the sulphated ash in the test for Heavy metals gives reaction (a) of
Sodium salts.
pH: 5.0 to 7.0, determined on 1.0 per cent w/v solution in carbon dioxide-free water.
Degree of substitution.
Take 1.0 g in 500ml conical flask, add 300ml of a 10 per cent w/v solution of sodium chloride, 25.0 ml of 0.1 M sodium hydroxide, stopper the flask and allow to stands for 5 minutes, shaking occasionally, Add 0.05ml of m-cresol purple solution and about 15ml of 0.1M hydrochloric acid from a burette. Insert the stopper and shake. If the solution is violet, add 0.1M hydrochloric acid in 1ml portions until the solutions becomes yellow, shaking after each addition. Titrate with 0.1M sodium hydroxide until the colour turns to violet.
Calculate the number of mill equivalents (M) of base required for the neutralization equivalent to 1g of dried substance.

Sodium chloride and sodium glycollate:
The sum of the percentage contents of sodium chloride and sodium glycollate is not more than 0.5 per cent, calculated on the dried basis.
Sodium chloride:
Place 5.0 g in a 250ml conical flask, add 50ml of water and 5 ml of strong hydrogen peroxide solution and heat on a water-bath
for 20 minutes stirring occasionally to ensure total hydration. Cool, add 100ml of water and 10ml of nitric acid. Titrate
with 0.05 M silver nitrate determining the end point potentiometrically. Using a silver indicator electrode and a
double junction reference electrode containing a 10 per cent w/v solution of potassium nitrate in the outer jacket and a standard filling solution in the inner jacket and stirring constantly.
1 ml of 0.05M silver nitrate is equivalent to 0.002922 g of NaCl.
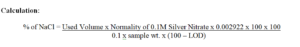
Reporting: Report in %.
Sodium glycollate:
Place 0.5g of the substance under examination in a 100ml beaker. Add 5ml of glacial acetic acid and 5ml of water and stir
to ensure total hydration (about 15 minutes). Add 50ml of acetone and1g of sodium chloride. Stir for several minutes to
ensure complete precipitation of the carboxymethyl- cellulose. Filter through a fast filter paper impregnated with
acetone into a volumetric flask, rinse the beaker and filter with 30 ml of acetone and dilute the filtrate to 100.0 ml
with the same solvent. Allow to stand for 24 hours without shaking. Use the clear supernatant to prepare the test solution.
Reference solution: Dissolve 0.1g of glycolic acid in 100ml of water. Use the solution within 30 days.
Transfer 1.0 ml, 2.0 ml, 3.0 ml and 4.0ml of the solution to separate volumetric flasks; dilute
the contents of each flask to 5.0 ml with water, add 5ml of glacial acetic acid, dilute to 100.0 ml with acetone and mix.
Transfer 2.0 ml of the test solution and 2.0 ml of each of the reference solutions to separate 25ml volumetric flasks.
Heat the uncovered flasks for 20 minutes on water –bath to eliminate acetone. Allow to cool and add 5.0ml of 2.7-dihydroxynaphthalene
solution to each flask. Mix, add a further 15.0ml of 2, 7-hydroxynaphthalene solution and mix again. Close the flasks with
aluminum foil and heat on a water-bath for 20 minutes. Cool and dilute to 25.0 ml with sulphuric acid.
Measure the absorbance of each solution at 540 nm . Prepare a blank using 2.0 ml of a solution containing 5 per cent v/v each
of glacial acetic acid and water in acetone. Prepare a standard curve using the absorbance obtained with the reference solutions.
From the standard curve and the absorbance of the test solution, determine the mass, in milligrams, of glycolic acid in the
substance under examination, and calculate the content of sodium glycollate from the expression;

Water soluble substances:
Disperse 10.0g in 800.0 ml of water and stir for 1 minute and stir for 1 minute every 10 minutes during the first 30 minutes. Allow to stand for 1 hour and centrifuge,
if necessary. Decant 200.0ml of the supernatant liquid onto a fast filter paper in a vacuum filtration funnel, apply to dryness and dry the residue at 100° to 105° for 4 hours.
Heavy Metals:
To the residue obtained in sulphated ash add 1ml of hydrochloric acid and evaporate on a water-bath. Take up the residue in 20ml of water, 12ml of
the solution complies with the limit test for heavy metals, Method (10 ppm). Prepare the reference solution using lead standard solution (1 ppm Pb).
Settling volume:
Place 75 ml of water in a 100ml graduated cylinder and add 1.5g of the substance under examination in 0.5g portions, shaking vigorously
after each addition. Dilute to 100.0 ml with water and shake again until the substance is homogeneously distributed. Allow to stand for 4 hours.
Microbial contamination:
Total microbial count, not more than 103 bacteria and 102 fungi per gram, determined by plate count. 10g is free from E. coli.
Sulphated ash:
Determined on 2.0g, using a mixture of equal volumes of sulphuric acid and water, and calculated on the dried basis.
.

Reporting: Report in %.
Analysis of vitamin B1 B6 B2 Nicotinamide and sodium pentothenate Injection
Analysis for Nandrolone Decanoate injection
Analysis of Dicyclomine and Diclofenac sodium Injection
standard testing procedure of Fexofenadine and Phenylephrine suspension
standard testing procedure of Piroxicam Injection
STP of Fungal Diastase and Papain capsules
standard testing procedure PVC
standard testing procedure glass ampoule
Standard testing procedure of Iron Sucrose Injection
Standard testing procedure lactose
Standard testing procedure mefenamic acid
standard testing procedure domperidone
standard testing procedure flavour mixed fruit
standard testing procedure dicyclomine hydrochloride
Standard testing procedure honey pure
standard testing procedure dextromethorphan hydrobromide
standard procedure of levocarnitine injection
Analysis of Ivermectin Suspension
standard testing procedure artemether injection
standard testing procedure artemether injection
standard testing procedure Carbocisteine syrup
standard testing procedure Phytomenadione injection
standard testing procedure serratiopeptidase
standard testing procedure starch IP
standard testing procedure sucrose refined sugar
standard testing procedure titanium dioxide
standard testing procedure tramadol hydrochloride
standard testing procedure zinc sulphate
standard testing procedure croscarmellose sodium
standard testing procedure colour erythrosine supra
standard testing procedure magnesium hydroxide
standard testing procedure diclofenac sodium
standard testing procedure dibasic calcium phosphate
standard testing procedure cyanocobalamin
standard testing procedure cholecalciferol
standard testing procedure Calcium carbonate oyster shell powder
standard test procedure Calcium Citrate
standard testing procedure Bronopol
standard testing procedure Bromhexine Hydrochloride
Standard Testing Procedure diclofenac sodium injection
Standard Testing Procedure Drotaverine Hydrochloride injection
Standard Testing Procedure Tranexamic acid injection
standard test procedure paracetamol infusion
standard test procedure ofloxacin and ornidazole infusion
standard test procedure ornidazole injection
standard test procedure Ondansetron injection
standard test procedure dextrose injection
standard test procedure ciprofloxacin injection
STP and analysis method of Ammonium Chloride
Analysis method of aceclofenac
analysis method of Losartan Potassium and Hydrochlorothiazide
analysis method of Linezolid Dry Syrup
analysis method of Drotaverine Hydrochloride and Mefenamic acid
Analysis method of Ceftriaxone Sodium and Sulbactam sodium Injection
analysis method of Cefepime and Tazobactam Injection
Analysis method of Hydroquinone Cream
Analysis method of Tacrolimus Ointment
Analysis method of Terbinafine HCL Cream
Analysis method of Mometasone Furoate and Fusidic Acid Cream
Analysis method of Disodium Hydrogen Citrate Syrup
Analysis method of Hydroquinone with Tretinoin Cream
Analysis method of Hydroquinone Tretinoin and Mometasone Furoate Cream
Analysis method of Sertaconazole Nitrate Cream
Analysis method of Halobetasol Propionate Cream
Analysis method of Povidone Iodine with Ornidazole Ointment
Analysis method of Eberconazole Cream
Analysis method of Luliconazole Cream
Analysis method of Fluconazole Gel
Analysis method of Ketoconazole Cream
Analysis method of Salbutamol and Choline theophyllinate Syrup
Analysis method of Methylcobalamin Injection
Analysis method of Piroxicam and paracetamol Injection
Analysis method of Alpha Beta Arteether Injection
Analysis method of Enrofloxacin Suspension
Analysis method of Levetiracetam Syrup
Analysis method of Sucralfate suspension
Analysis method of Sucralfate and Oxetacaine Suspension
Analysis method of Quinine Sulphate Suspension
Analysis method of Calcium Carbonate vitamin D3 Zinc Gluconate and Magnesium hydroxide suspension
Analysis method of Suspension of Tribasic Calcium phosphate with vitamin D3 and Vitamin B12
Analysis method of Calcitriol with calcium citrate Suspension
Analysis method of Oxyclozanide and Fenbendazole Suspension
Analysis method of Oxyclozanide and Levamisole Suspension
Analysis method of Triclabendazole and Ivermectin Suspension
Analysis method of Itraconazole Solution
Analysis method of Levocetirizine Dihydrochloride syrup
Analysis method of Iron Calcium Vitamin D3 Folic Acid Vitamin B12 Suspension
Analysis method of Ferrous Ascorbate Cyanocobalamin and Folic Acid Suspension
Analysis method of Ambroxol Hydrochloride Drops
Analysis method of Ferrous Ascorbate with Folic Acid suspension
Analysis method of Piracetam Syrup
Analysis method of Rafoxanide and Levamisole suspension
Analysis method of Zinc gluconate Syrup
Analysis method of Magaldrate Simethicone and Oxetacaine suspension
Analysis method of mefenamic acid and paracetamol suspension
Analysis method of Cholecalciferol Drops
Analysis method of Racecadotril suspension
Analysis method of Deflazacort Suspension
Analysis method of Montelukast sodium and levocetirizine Dihydrochloride Syrup
Analysis method of Iron and Folic Acid Syrup
Analysis method of Cyproheptadine Hydrochloride and Tricholine Citrate Syrup
Analysis method of Levofloxacin Hemihydrate Ornidazole and Vitamin E Solution
Analysis method of Albendazole and ivermectin in oral liquid